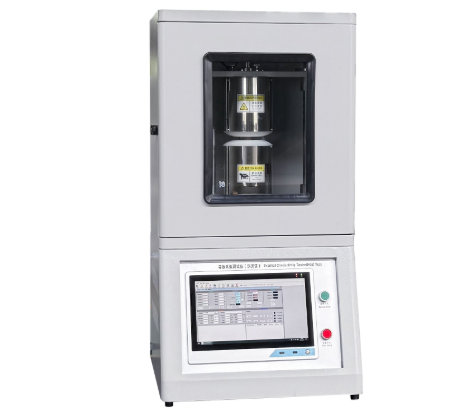
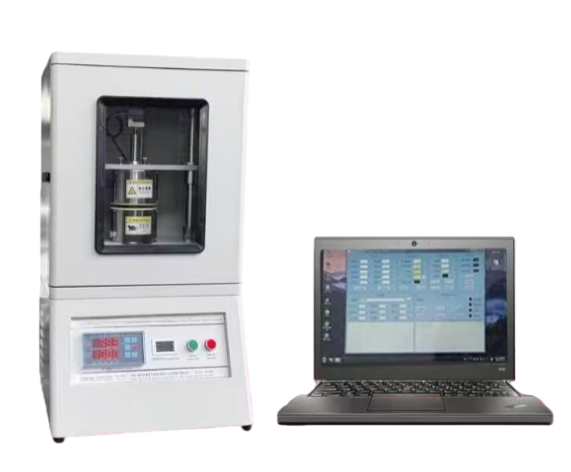
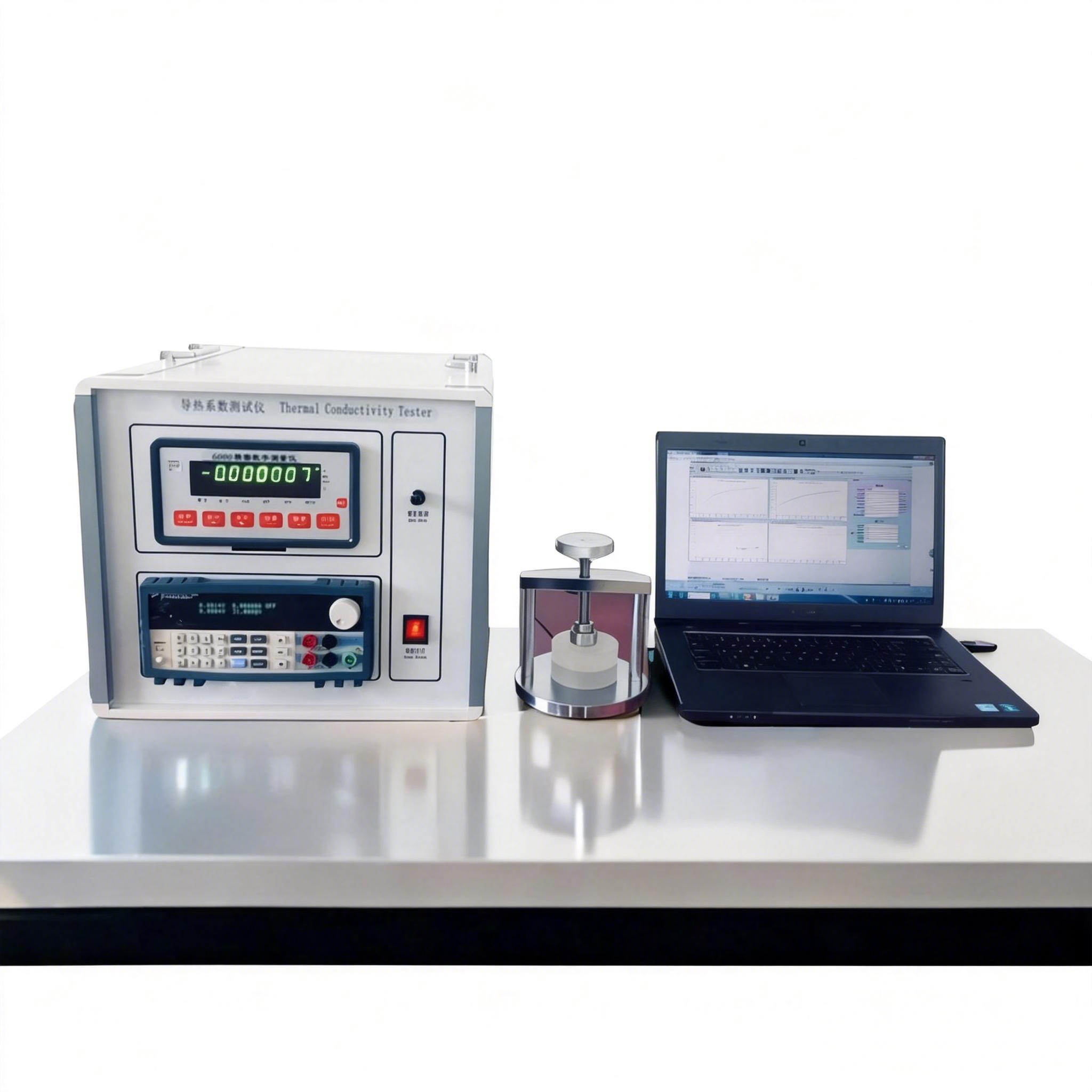
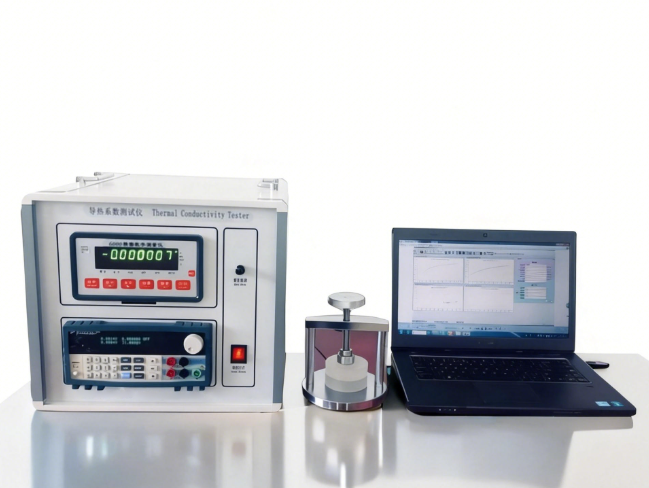
Automatic High-Temperature Specific Heat Capacity Tester

Fully Automatic High-Temperature Specific Heat Capacity Tester is a state-of-the-art instrument designed for measuring the specific heat capacity of solid materials at elevated temperatures. Using the mixed method and fully automated computer control, it accurately records temperature changes of the sample and calorimeter to calculate specific heat.
The tester is widely used in scientific research and teaching laboratories to investigate thermal properties of solid materials. For high-temperature, oxidation-prone samples, an atmosphere protection system can be added. The tester fully complies with GJB 330A-2000: Test Methods for Specific Heat Capacity of Solid Materials and reduces human error while improving test accuracy.
Application
The tester is suitable for:
Scientific research laboratories studying thermal properties of solids.
University and educational laboratories for teaching and demonstration purposes.
Industrial R&D to evaluate high-temperature thermal behavior of metals, ceramics, and composites.
Measurement of specific heat capacity of powders and solid samples under controlled atmospheres (e.g., argon).
Typical sample types include:
Metals, alloys, and ceramics
High-temperature refractory materials
Powders and granular solids
Materials requiring protective atmospheres during heating
Standards
GJB 330A-2000 – Test Methods for Specific Heat Capacity of Solid Materials
Parameters
| Item | Specification |
|---|---|
| Specific heat capacity range | 0.05–5 kJ/(kg·K) |
| Measurement accuracy | Solid ≤ 1% ± 0.002; Powder ≤ 2% ± 0.002 |
| Temperature range | 100–800°C (resistance wire heating, calorimeter heat capacity ~1000 J/K, atmospheric) 200–1350°C (silicon carbide tube heating, calorimeter heat capacity ~1500 J/K, argon atmosphere) |
| Sample size | Solid: φ11–φ14 × 20–40 mm Powder: ~6 cm³ |
| Calorimeter resolution | 0.001°C |
| Measurement method | Mixed method |
| Power supply | 220V/50Hz, 3 kW |
| Control system | Intelligent PID, fully automated computer control |
| Instrument configuration | Main unit, software, communication interface and data cable, high-precision thermostatic water bath, desktop computer (per contract) |
Features
Fully automated testing: Software-controlled data acquisition, calculation, and report generation.
High accuracy: Minimizes human error, achieving ≤1% for solids and ≤2% for powders.
Wide temperature range: 100–1350°C with optional protective atmosphere.
Mixed method testing: Accurate measurement using calorimeter and temperature monitoring.
Versatile sample types: Supports both solid and powder materials.
Intelligent PID control: Maintains precise temperature conditions throughout the test.
Accessories
Main instrument
Analysis software (Chinese & English version)
Communication interface and data cable
High-precision thermostatic water bath
Desktop computer (per contract)
Test Procedures
Prepare the solid or powder sample according to the specified dimensions.
For high-temperature, oxidation-prone samples, connect the protective atmosphere system (e.g., argon).
Hang the solid sample in the tubular heating furnace and heat to the target experimental temperature.
Drop the heated sample into the calorimeter.
The computer system automatically records temperature changes of both the sample and calorimeter.
The software calculates the specific heat capacity and generates a report.
Maintenance Information
Keep the calorimeter and heating elements clean and free from contamination.
Regularly check connections, data cables, and communication interfaces.
Calibrate the system periodically using standard reference materials.
Inspect the protective atmosphere system for leaks when testing high-temperature oxidation-prone samples.
Store the instrument in a dry, stable-temperature environment to protect electronics and heating components.
FAQ
1. What type of samples can this tester test?
This tester can measure both solid and powder materials, including metals, ceramics, alloys, and granular samples. Solid samples should have a diameter of 11–14 mm and height of 20–40 mm, while powders require approximately 6 cm³. For oxidation-prone materials, the instrument can be equipped with an argon atmosphere system to prevent sample degradation at high temperatures.
2. How is the specific heat capacity measured?
The tester uses a mixed method, where the sample is first heated in a tubular furnace to the experimental temperature and then dropped into a calorimeter. The system records temperature changes of both the sample and calorimeter. Using these measurements, the software calculates the specific heat capacity automatically. The fully automated process reduces human error and ensures high precision.
3. What is the temperature range for testing?
For atmospheric measurements, the instrument can operate between 100–800°C using resistance wire heating. For high-temperature applications with an argon protective atmosphere, it can operate between 200–1350°C with silicon carbide tube heating. Temperature control and monitoring are handled by an intelligent PID system to ensure stability and accuracy.
4. How accurate is the tester?
For solid materials, the measurement accuracy is ≤1% ± 0.002. and for powders, ≤2% ± 0.002. The instrument uses computer-controlled data acquisition and intelligent PID temperature regulation, reducing human error and providing consistent, repeatable results for research and industrial applications.
Leave Message Get Price