-
What is the ASTM standard for tensile strength rubber?
Edited by:Read:ASTM D412 is the standard test method for testing the tensile properties of rubber. This standard is widely recognized and used in the rubber industry to determine the tensile strength, elongation, and other mechanical properties of rubber materials.
ASTM D412 specifies the procedures for determining the tensile properties of vulcanized rubber and thermoplastic elastomers. It provides guidelines for preparing test specimens, conducting the test, and calculating various tensile properties.
The standard covers the determination of several tensile properties, including:
1. Tensile strength: The maximum tensile stress that a rubber specimen can withstand before breaking.
2. Elongation at break: The percentage increase in length of the rubber specimen at the moment of rupture.
3. Modulus at a specified elongation: The amount of force required to stretch the rubber specimen to a specific elongation.

4. Stress-strain behavior: The relationship between stress (force per unit area) and strain (percentage change in length).
5. Set properties: The extent to which the rubber specimen maintains deformation after being stretched and released.
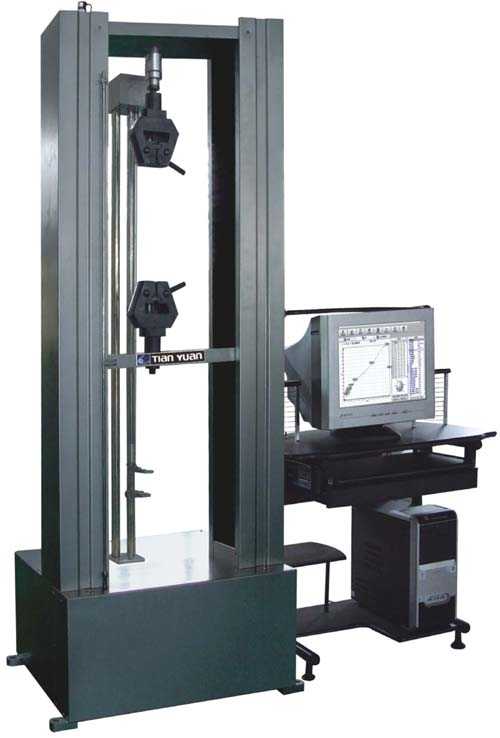
ASTM D412 provides detailed instructions for conducting these tests using different types of testing equipment, such as a universal testing machine. It also includes requirements for sample preparation, test conditions, and data reporting.
By following ASTM D412, manufacturers, researchers, and quality control personnel can ensure consistent and reliable measurement of the tensile properties of rubber materials, allowing for accurate characterization and comparison of different rubber compounds and products.
In summary, the ASTM D412 standard is the recognized industry standard for testing the tensile strength of rubber. It provides guidelines for conducting tests and ensures accurate and consistent results. By adhering to this standard, manufacturers and researchers can evaluate the mechanical properties of rubber materials and make informed decisions regarding their use in various applications.
- 2024-04-19Paper ring compression strength tester standards
- 2024-04-19Cupping tester standards
- 2024-04-19Rubber and plastic tensile tester standards
- 2024-04-19Taber 1750 wear-resistant tester standards
- 2024-04-19Stone Chip Resistance Gravelometer standards
- 2024-04-18Diaper absorption speed tester standards
- 2024-04-18Diaper leakage tester technical indicators
- 2024-04-18Paint film impact resistance tester standards
- 2024-04-18Low temperature brittleness tester principle
- 2024-04-18Battery separator permeability tester technical indicators