-
What are some common issues that can affect the accuracy of the Random Tumble Pilling Tester results?
Edited by:Read:There are several issues that can affect the accuracy and reliability of the test results when using a Random Tumble Pilling Tester. Here are some common issues to be aware of:
1. Inconsistent sample preparation: Inconsistent sample preparation can lead to variations in the size, shape, and surface characteristics of the samples, which can affect the test results. It is important to carefully follow the sample preparation instructions provided by the instrument manufacturer to ensure that the samples are prepared consistently.
2. Improper sample installation: Improper sample installation, such as using too much or too little adhesive tape or not securing the sample tightly enough, can result in variations in the test results. It is important to follow the sample installation instructions provided by the instrument manufacturer to ensure that the samples are installed correctly.
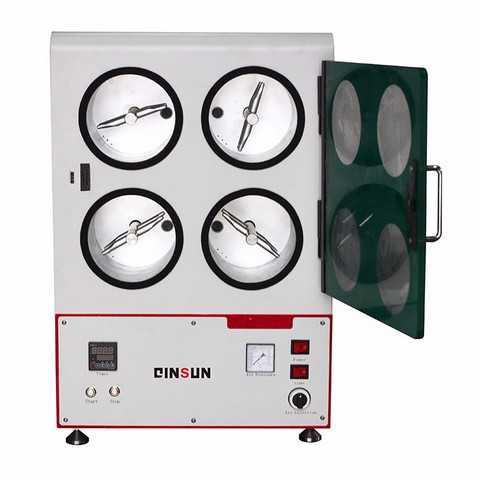

3. Inaccurate test conditions: Inaccurate test conditions, such as incorrect test duration, speed, or temperature, can also affect the test results. It is important to verify the test conditions and adjust them if necessary to ensure that they are consistent with the test standard or protocol being used.
4. Sample contamination: Contamination of the samples with dust, oil, or other substances can affect the test results. It is important to keep the samples and the instrument clean and free of contaminants to ensure the accuracy of the test results.
5. Instrument calibration: The accuracy of the instrument can also affect the test results. It is important to calibrate the instrument regularly according to the manufacturer's instructions to ensure that it is operating correctly.
6. Operator error: Operator error, such as incorrect handling of the samples or incorrect recording of the test results, can also affect the accuracy of the test results. It is important to train operators on proper instrument operation and data recording to minimize the risk of operator error.
Overall, it is important to carefully follow the instrument manufacturer's instructions and the test standard or protocol being used to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the test results.
- 2024-04-19Paper ring compression strength tester standards
- 2024-04-19Cupping tester standards
- 2024-04-19Rubber and plastic tensile tester standards
- 2024-04-19Taber 1750 wear-resistant tester standards
- 2024-04-19Stone Chip Resistance Gravelometer standards
- 2024-04-18Diaper absorption speed tester standards
- 2024-04-18Diaper leakage tester technical indicators
- 2024-04-18Paint film impact resistance tester standards
- 2024-04-18Low temperature brittleness tester principle
- 2024-04-18Battery separator permeability tester technical indicators