-
Investigation and Interpretation of Mask Filtration Efficiency Testing Methods
Edited by:Read:At present, there are many types of masks circulating in the market, including protective filter masks such as dust-proof, toxic gas-proof, and germ-proof. According to the specific needs of personnel in various industries, the country has issued corresponding mask standards to regulate the domestic mask market. Most of the protective filter mask standards implemented in my country are mandatory product standards, and filtration efficiency is an important test item, so it is very important to study the filter efficiency of protective filter masks.
Masks can be divided into N and P (or KN and KP) according to different filtering performances. N (or KN) is only suitable for filtering non-oily particles, and P (or KP) is suitable for filtering oily and non-oily particulates.

Among them, NIOSH divides anti-particulate respirators or filter elements into three categories: N, R, and P according to the nature of the protected object and the length of time to prevent oily particles: N type is used to protect non-oily particles; R type and P type can be used for protection Non-oily particles and oily particles (R type filter elements have a shorter use time limit than P type filter elements, generally 8h, and P type filter elements have a longer use time, generally made by the manufacturer. Suggestions for use time ).
For the detection of the filtration efficiency of salt particles, NaCl aerosol is used, while for the detection of oily particle filtration efficiency, DOP or paraffin oil or other oil particles with similar properties are generally used.
Filtration Mechanism:
(1) Brownian motion: Because the particle size is too small, it is vulnerable to the constant impact of other gas molecules, causing their trajectory to be irregular Brownian motion and adsorbed on the surface of the fiber. The smaller the particle, the stronger the effect.
(2) Interception: The size of the particle is too large to penetrate the gap of the fiber, and then it is directly captured by the surface of the fiber. The larger the particle size, the better the effect.
(3) Inertial impact: Particles of different masses, coupled with high speed, produce different inertias, so that the particles cannot bypass the surface of the filter material with the air flow and leave the flow line, collide with the surface of the fiber and fall, the greater the mass And the faster the particle, the stronger the force.
(4) Electrostatic adsorption: Charge the fiber to induce ultra-fine particles to adsorb on the surface of the fiber. For particles with smaller particle size and light weight, it is easier to be attracted.
(5) Sedimentation: Direct sedimentation caused by the gravity of the particles themselves, and captured by the filter material, the greater the mass, the more chances.
Mask filtration efficiency testing equipment:
Mask Particle Filtration Efficiency (PFE) Tester
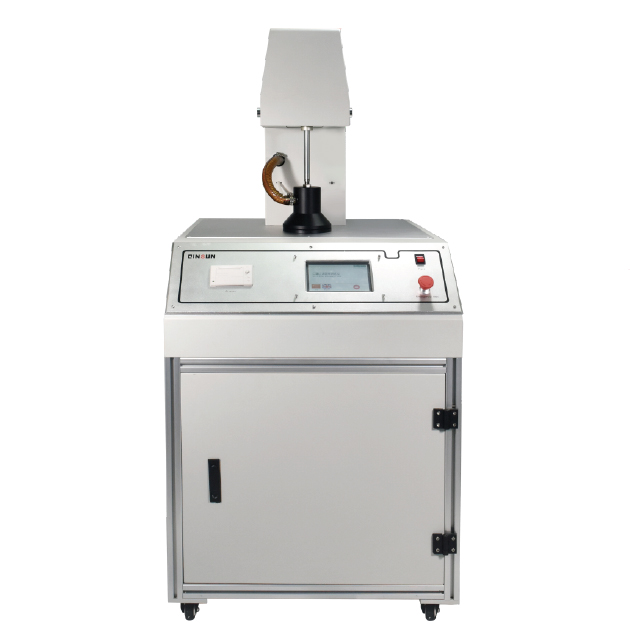

Masks Bacterial Filtration Efficiency (BFE) Tester

- 2024-04-19Paper ring compression strength tester standards
- 2024-04-19Cupping tester standards
- 2024-04-19Rubber and plastic tensile tester standards
- 2024-04-19Taber 1750 wear-resistant tester standards
- 2024-04-19Stone Chip Resistance Gravelometer standards
- 2024-04-18Diaper absorption speed tester standards
- 2024-04-18Diaper leakage tester technical indicators
- 2024-04-18Paint film impact resistance tester standards
- 2024-04-18Low temperature brittleness tester principle
- 2024-04-18Battery separator permeability tester technical indicators